
Herbivore, omnivore and carnivore • Teacha!
Background There are three main dietary groups in mammals: carnivores, omnivores, and herbivores. Currently, there is limited comparative genomics insight into the evolution of dietary specializations in mammals. Due to recent advances in sequencing technologies, we were able to perform in-depth whole genome analyses of representatives of these three dietary groups. Results We investigated the.

Herbivore, Carnivore & Omnivore Types of animals What's the difference? YouTube
Step 3: Sort Animals. Let your child sort the animals according to how she believes the animals are classified. Talk to her about the different foods each animal eats (or you think they eat!). Remember that if you get one in the wrong spot, it's no biggie. This game stumps some of the best of us.
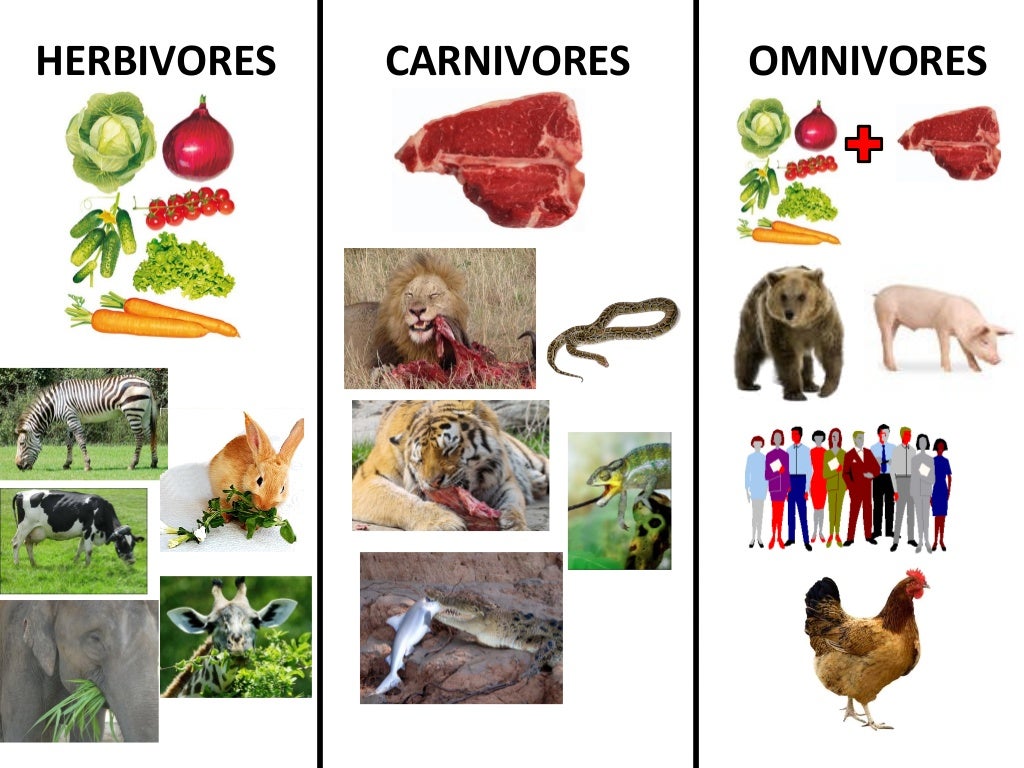
Herbivores, carnivores and omnivores
Animals that are plant eaters are called herbivores, meat-eaters are carnivores, and animals who eat both plants and meat are called omnivores. See the fact file below for more information on Herbivores, Carnivores, and Omnivores or alternatively, you can download our 29-page Herbivores, Carnivores, and Omnivores worksheet pack to utilise.

Carnivore, Herbivore, Omnivore. What’s the Difference? Trilobit's Blog
Examples of omnivores. From left to right: humans, dogs, pigs, channel catfish, American crows, gravel ant Among birds the Hooded crow is a typical omnivore. An omnivore (/ ˈ ɒ m n ɪ v ɔːr /) is an animal that has the ability to eat and survive on both plant and animal matter. Obtaining energy and nutrients from plant and animal matter, omnivores digest carbohydrates, protein, fat, and.

PPT Carnivores, Herbivores, and Omnivores PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2657311
Omnivores are animals that eat both plant- and animal-derived food. In Latin, omnivore means to eat everything. Humans, bears (shown in Figure 3a), and chickens are example of vertebrate omnivores; invertebrate omnivores include cockroaches and crayfish (shown in Figure 3b). Figure 3. Omnivores like the (a) bear and (b) crayfish eat both plant.
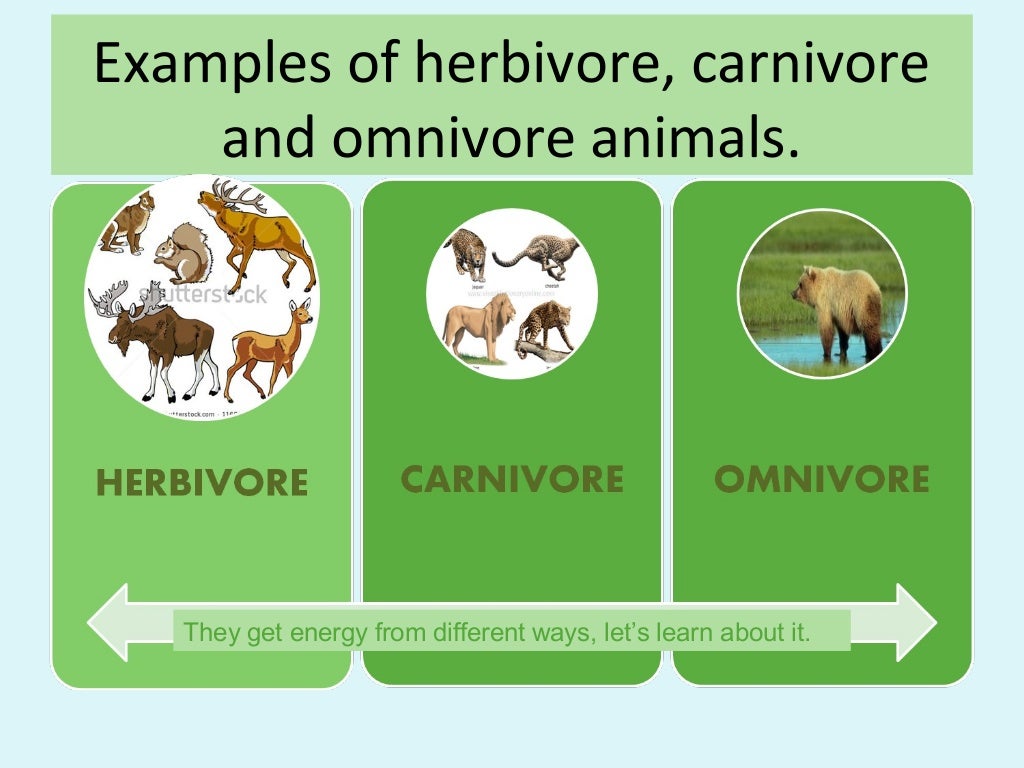
Herbivore, carnivore and omnivore animals
Omnivores are animals that eat both plants and meat. Some examples of omnivores include pigs, opossums, humans, raccoons, bears, mice, and ants. Omnivores will usually eat a wide variety of foods to get the nutrients they need to survive. For example, omnivores might eat grains like wheat and corn, as well as meat.

Herbivore, Carnivore, Omnivore Lessons Blendspace
Credits. Everything - mammals, reptiles, insects, and birds - needs to eat! What they eat puts them into one of three categories: herbivore, carnivore, and omnivore. National Geographic Explorer and lion conservationist Paola Bouley breaks these terms down into bite-size pieces.

KS1 Carnivore, Omnivore, Herbivore sorting Teaching Resources
Herbivores are animals whose primary food source is plant-based. Examples of herbivores, as shown in Figure 1 include vertebrates like deer, koalas, and some bird species, as well as invertebrates such as crickets and caterpillars. These animals have evolved digestive systems capable of handling large amounts of plant material.

Classification Omnivore/Carnivore/Herbivore
Figure 34.2.1 34.2. 1: Examples of herbivores: Herbivores, such as this (a) mule deer and (b) monarch caterpillar, eat primarily plant material. Some herbivores contain symbiotic bacteria within their intestines to aid with the digestion of the cellulose found in plant cell walls. Omnivores are animals that eat both plant- and animal- derived food.

an image of animals that are in the same language as humans and dogs or cats
Food Web Exploration. Hand out copies of a food web (or food chain) as herbivore, omnivore, and carnivore worksheets.Ask students to use the food web to figure out which animals are herbivores, which ones are omnivores, and which ones are carnivores.
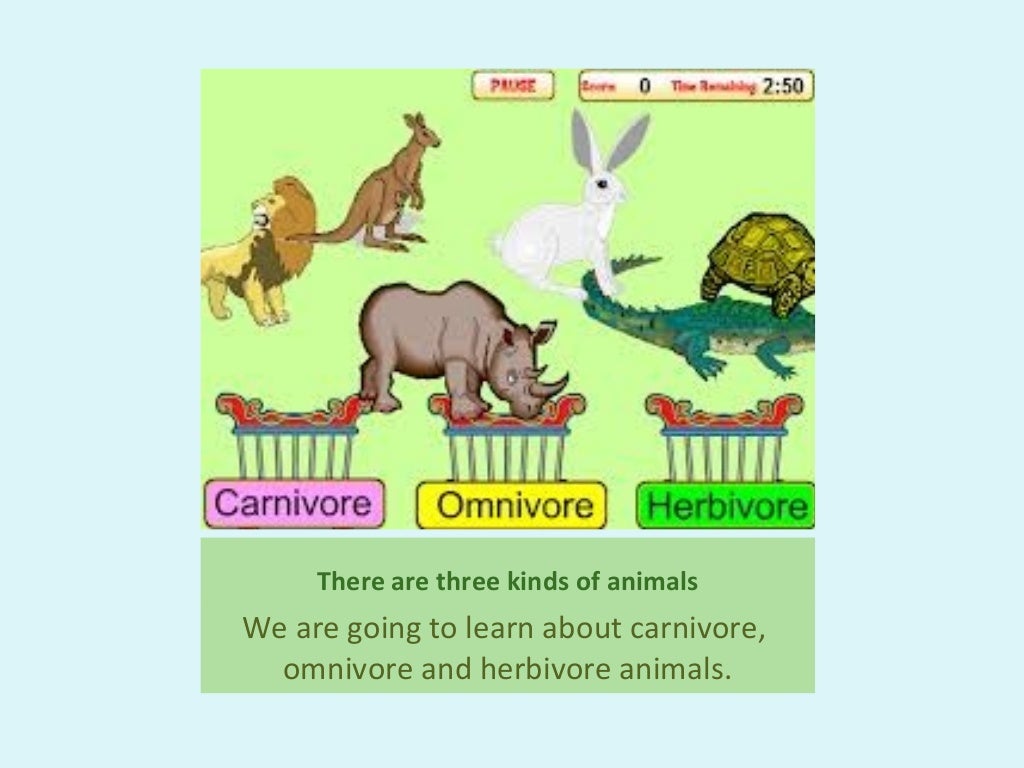
Herbivore, carnivore and omnivore animals
Examples of carnivorous animals include lions, wolves, and bears. Herbivores are animals that primarily eat plants. They may graze on grass and other vegetation, or they may browse on leaves, fruits, and other plant parts. Examples of herbivorous animals include deer, rabbits, and cows. Omnivores are animals that eat both plants and animals.

PPT Carnivores, Herbivores, and Omnivores PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5383483
Introduction to the Diets. The Herbivores, Carnivores, Omnivores lesson plan contains four content pages. The first page explains to students what the suffix -vore means. The suffix means to eat or devour. The actual food something eats or devours depends on the prefix. This lesson describes three different diets.
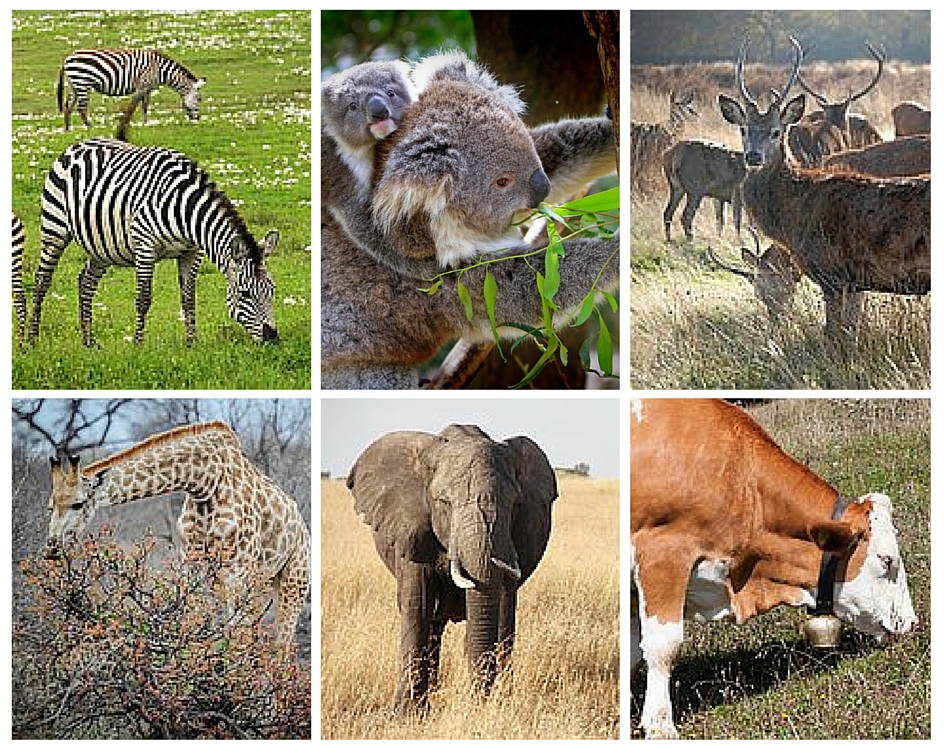

Difference Between Herbivores Carnivores and Omnivores
#herbivoresong #songsforteaching #sciencesongsI wrote this one for my science unit on the food chain. It helps teach about herbivores, carnivores, and omnivo.
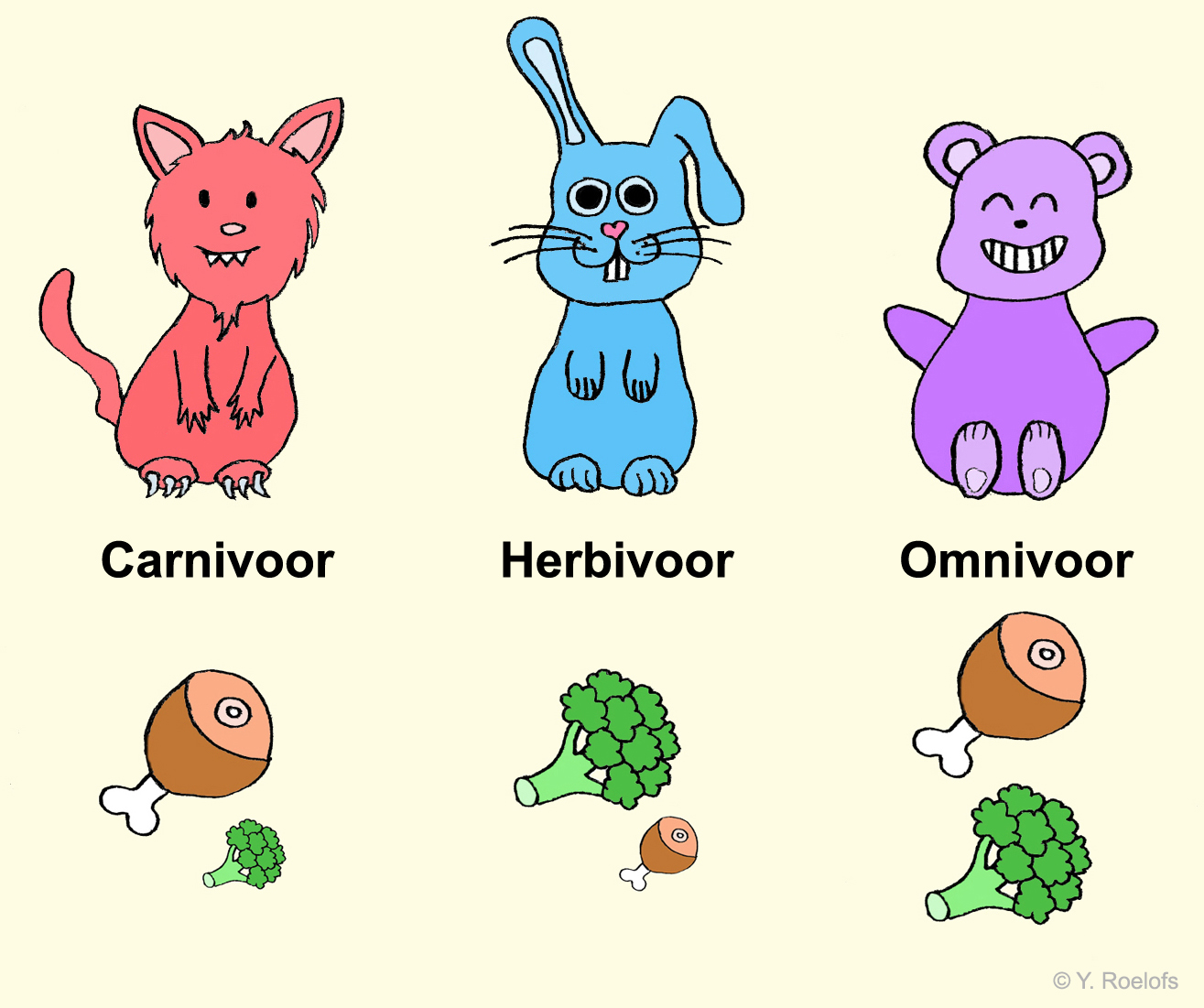
Yvonne's Biologieblog Voedselkeuze
Herbivores: animals that only eat plants. Carnivores: animals that only eat meat. Omnivores: animals that eat both plants and meat. Teach Starter has created a sorting activity for your students to practice categorizing animals according to their diet. This resource includes high-quality photographs of animals on each of the 24 sorting cards.

Carnivore, Herbivore, Omnivore KS1 Poster by PlanBee
From the Education Resource Library: National Geographic Explorer Paola Bouley defines and explains the differences between herbivores, carnivores and omnivo.

Herbivore, omnivore and carnivore • Teacha!
This isn't always the case, but herbivores more typically have flatter teeth for grinding up vegetation, while carnivores will have sharp teeth for tearing up meat. Many omnivores will have some combination of the two, allowing for easier eating and digestion of their food sources. 👍. Animals fall into three distinct groups based upon what.